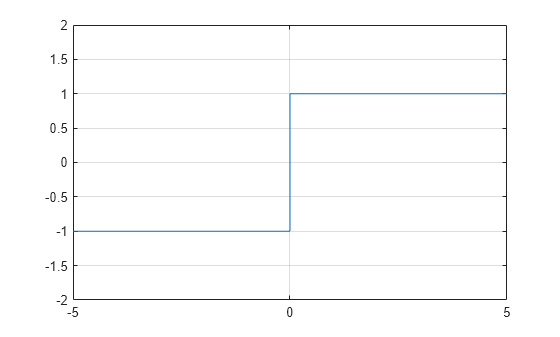
Y = sign( x ) returns an array Y the same size as x , where each element of Y is:
Find the sign function of a number.
sign(2)
ans = 1
Find the sign function of the values of a vector.
V = [-11 0 1.5 Inf NaN]; sign(V)
ans = 1×5 -1 0 1 1 NaN
Find the sign function of the values of a matrix.
M = magic(3) - 5; sign(M)
ans = 3×3 1 -1 1 -1 0 1 -1 1 -1
Find the sign function of a complex number.
z = 4 - 3*i; sign(z)
ans = 0.8000 - 0.6000i
Plot the sign function and show its behavior at the zero-crossing. Use eps to represent values just above and below 0 .
x = [-5 -eps(1) 0 eps(1) 5]; y = sign(x); plot(x,y) ylim([-2 2]) grid on
Plot real and imaginary parts of the sign function over - 3 < x < - 3 and - 3 < y < 3 .
v = -3:0.1:3; [x, y] = meshgrid(v); z = x + 1i*y;
Find the real and imaginary parts of the sign function of z .
s = sign(z); re = real(s); im = imag(s);
Plot the real and imaginary parts.
surf(x,y,re) title('Real part of sign function') xlabel('x') ylabel('y')
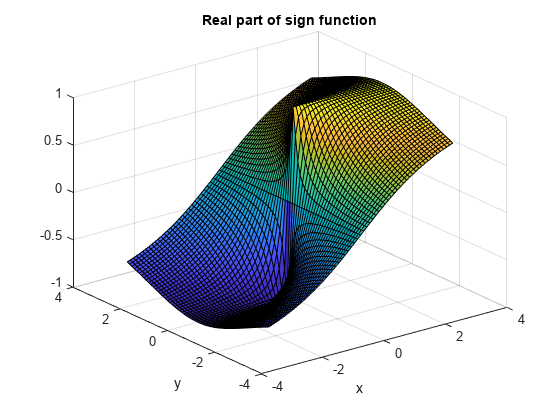 ylabel y contains an object of type surface." width="583" />
ylabel y contains an object of type surface." width="583" />
figure(2) surf(x,y,im) title('Imaginary part of sign function') xlabel('x') ylabel('y')
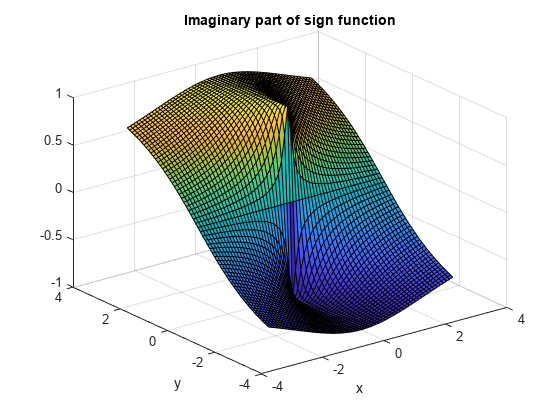 ylabel y contains an object of type surface." width="583" />
ylabel y contains an object of type surface." width="583" />
Input, specified as a scalar, vector, matrix, or multidimensional array.
If an element of x is NaN , then sign returns NaN in the corresponding element of the output.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical | duration
Complex Number Support: Yes
The sign function fully supports tall arrays. For more information, see Tall Arrays.
This function fully supports thread-based environments. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions in Thread-Based Environment.
The sign function fully supports GPU arrays. To run the function on a GPU, specify the input data as a gpuArray (Parallel Computing Toolbox) . For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions on a GPU (Parallel Computing Toolbox) .
This function fully supports distributed arrays. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions with Distributed Arrays (Parallel Computing Toolbox) .
Introduced before R2006a